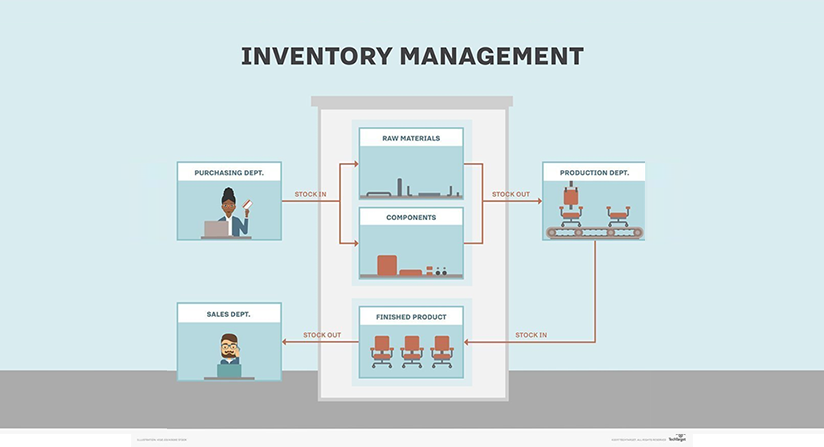
It’s difficult to determine if an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is right for your business. It provides many advantages, including a unified database with integration across departments. Implementing an ERP can provide a significant return on investment due to factors such as business intelligence and efficiency gains.
Manufacturers often need functionality specific to their industry. Manufacturing ERP provides more value as it has business and manufacturing operations modules. Understanding how companies use different ERP features to deliver value is helpful. The eight use cases below show how these unique companies benefit from the implementation of manufacturing ERP.
Use Case #1 – Medical Device Manufacturer Needs Integration with Inventory and Production
Before:
A small manufacturing company is getting ready to close a fundraising deal. It will more than double its staff. They are currently using QuickBooks and manual methods to handle business operations. They need to run various reports, including some for the FDA, which is challenging.
They need an integrated system to manage their inventory and shop floor to handle this increased production. They also would like to automate the purchase order process and vendor management. And they want their sales team to be able to submit orders for production within the same system.
After:
Their ERP system has eliminated redundancy and improved efficiency with full integration. Its powerful reporting tools make it simple for them to provide the required reports to the FDA. Sales can now create quotes and easily change them into sales orders. Those sales orders are then converted into production orders for a streamlined process.
Their ERP system has optimized and automated their production tasks. They ramped up production to accommodate their new project. Real-time visibility into safety stock, re-order points, cycle counts, and demand planning ensures their deliveries are on time.
As goods are received, inventory levels automatically update, and purchasing is notified immediately. Purchasing is using intuitive dashboards to track vendor performance in real time. They have enhanced vendor relationships because of the improved communication provided by the system.
Use Case #2 – Make-to-Order Industrial Machinery Company Needs Job Cost and MRP
Before:
They are unable to determine job costs quickly. It’s difficult for them to keep the proper materials in stock to meet production demand. Their shop floor staff are manually tracking how they spend their time, which often isn’t accurate. Currently, they handle all financial transactions using spreadsheets which is time-consuming and inefficient.
After:
With ERP, they have been able to transform their shop floor, connect to machinery, check employee performance, and improve workflow. Without leaving their desks, shop floor operators note when a job starts, stops, and if any machine downtime occurs, and then move on to their next job. Managers are now easily tracking productivity by both operator and machine.
The robust financial management system in their ERP handles transactions efficiently. Month-end closings are faster, providing more time to work on other projects. They now have an accurate picture of the business and get a cash flow forecast at any time. Management makes more informed decisions which helps them better plan and grow.
Use Case #3 – Midsized Manufacturer Wants Full Integration
Before:
This manufacturer needs help managing its growing business that has an old DOS-based system. It can’t track production, create work orders, use barcodes, or manage inventory. It also doesn’t handle job costing, and it is difficult for them to keep track of supplies or see how well the business is performing. Everything is inefficient and disjointed.
After:
Their manufacturing ERP system now tracks, controls, and documents the product journey from raw materials to finished goods. They know the quantities of materials used in the production process, the number of items produced, and how many products pass or fail quality tests, all without human intervention. They also have complete visibility into job costs by tracking everything as it moves through the shop.
Now all of their processes connect to a single database. Everyone works from the same information. They scan barcodes during putaway, procurement, picking, and shipping of products. As a result, they have fewer errors and improved inventory visibility. Their new system’s user interface made learning easy for their employees.
Use Case #4 – Small Electronics Manufacturer Needs Improved Workflow
Before:
Their current software’s focus is financials, and it doesn’t have manufacturing functionality. They are trying to improve their workflow but need a software system to help. They want all their departments linked together.
Right now, they can’t plan for production, manage their supply chain, or track inventory needs. They have a quality checklist they review for every product they make, which is time-consuming.
After:
With their ERP system in place, everything is connected and streamlined. Their optimized workflow lets them pivot fast as business needs change. Supply chain management functionality analyzes demand to identify potential problems. They identify any quality issues and proactively resolve them. It has become easy to comply with industry, regulatory, and customer requirements.
Use Case #5 – Contract Manufacturer Working from Spreadsheets Needs Better Tracking Capabilities
Before:
Everything they do is Excel-based. They don’t have a reliable system to track their materials, inventory, labor, and work orders. They also need a way to quickly generate quotes, track production to control their operations better, and they need something to manage their shop floor workflow.
After:
With their manufacturing ERP, all processes are automated and tracked. The system generates and assigns shop floor tasks to staff. They have been able to identify workflow improvements and increase efficiency. They use the bill of materials functionality to create a list of the resources needed to quote jobs accurately.
Detailed purchasing data has allowed them to lower costs. They easily compare vendor pricing to identify savings opportunities. Managers make more intelligent decisions using customizable reports. Synchronization of accounting and inventory ensures optimal levels of materials. The business has become less complex and better organized and has eliminated most paperwork.
Use Case #6 – High-End Upholstery Manufacturer Needs Project Customization
Before:
All their production is made-to-order and is created on a project-by-project basis. They are using QuickBooks, spreadsheets, and an ERP system that can’t handle their business needs. Their biggest challenge is the inability to provide project customizations. They must effectively plan their production based on materials, labor, and machinery costs. They also need to be able to manage everything from procurement to production and delivery.
After:
With product configurator functionality, they respond quickly to customer requests for quotes and easily accommodate custom orders. Each configuration is assigned a unique item code to simplify tracking and repeat orders. The system then automatically creates sales quotes/orders, BOMs, and routings.
Managers are now tracking productivity by operator and machine from their dashboards. They see the operation status in real time, as well as the quantity produced. They compare machine capacity against actual production and develop delivery times to match. End-to-end processes allow purchasing to request, approve, buy, and receive materials as needed. They make better purchasing decisions with visibility of vendor performance.
Use Case #7 – Fast Growing Company Needs Quick Implementation of Full-Suite Cloud-Based ERP
Before:
The company plans to double revenue with the orders they currently have pending now. They need a full-suite ERP system to handle as many processes as possible. Currently, they only have an accounting system in place. They can’t take care of existing quotes without an ERP system, so their need is immediate.
They are looking for full MRP and MES modules for all customer manufacturing. They need to handle order tracking, planning, scheduling, and sourcing. They also want to track orders in real-time and prevent manufacturing bottlenecks. They need Financial Management, CRM, Quality Management, and Warehouse Management. With an operation in France, they also need multi-currency and language capabilities. They are searching for an e-commerce tool to help them sell their products online.
After:
They chose a cloud-based manufacturing ERP for its quick implementation time. They now access business-critical applications at any time from any location. Their cloud ERP has optimized processes across their business operations. They can easily track, plan, schedule, and source orders in the system. They have real-time shop floor insight to react immediately to production issues. They have implemented manufacturing best practices for improved shop floor workflow.
Their ERP system handles their business and manufacturing operations. It automates accounting processes, manages cash flow, controls budgets, and monitors job costs. As a multi-national company, they now process payroll in multiple currencies and languages.
They track inventory in the warehouse, and their sales team manages quotes and customer follow-ups on the road using a mobile app. Quality processes connect with manufacturing and distribution for better control and traceability. They now sell products on their website with e-commerce functionality and have reduced their sitting stock.
Use Case #8 – Metal Fabrication Company Needs Better Data for Business Decisions
Before:
Currently, they are using QuickBooks and SmartSheet. They can’t receive or share information with the shop floor. They want to determine material costs without throwing a dollar-per-pound number at it. They plan to double their staff and need something suited to a more extensive operation. They need to forecast total costs better to quote for their clients accurately. They also need real-time data on production status and estimated time to completion to provide to management.
After:
Their manufacturing ERP connects their accounting practices to their dynamic manufacturing processes. They manage cash flow, control budgets, and track job costs. Using supply chain demand data, they create schedules for production, purchasing, and inventory. Shop floor managers identify variances, calculate costs, improve operations, and reduce waste. All information can be easily obtained via reports and provided to upper management.
Conclusion
Hopefully, these use cases provided insight into how ERP can help manufacturers with different challenges. OptiProERP manufacturing ERP is fully integrated with SAP Business One providing robust business and manufacturing functionality. It is capable of handling each of these use cases. Please get in touch with us or view this product tour to learn more about manufacturing ERP or OptiProERP.
If you begin reviewing ERP software, you’ll find pricing gets complex. This free guide and template can help you identify all of the costs to consider.
Follow Us