Acquiring goods from vendors and suppliers is one of the critical and routine tasks for manufacturers. Managing, planning, and tracking finance is very important when it comes to the outflow of cash. Otherwise, it can adversely affect a company’s bottom line.
Procurement and purchasing are terms interchangeably used in manufacturing but are distinct activities. In this blog, we will see how purchasing and procurement differ.
Procurement
Procurement is a long-term, holistic approach that includes acquiring goods and services from external sources, identifying needs, negotiating, receiving, and inspecting goods. From invoicing, making payments, and managing suppliers, procurement saves time while building positive supplier relationships. In other words, procurement includes the steps required before, during, and after purchasing commodities from the vendor.
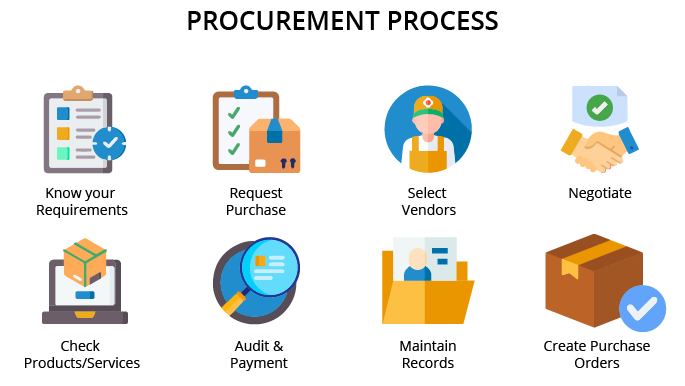
Steps in the Procurement Process
1. Identify which goods and services the organization needs
All business departments affected by purchasing decisions should provide information on needed items. Delving into the product’s specifications, such as technical details, part number, or service characteristics, is essential. The items can be new, restocked goods, or subscription renewals.
2. Submit a purchase request
When an employee or a department needs to procure products from a new supplier, they make a formal request, known as a Purchase Request or Purchase Requisition. Managers submit a Purchase Request to the finance team to ensure the purchases are within budget.
3. Assess and select vendors
Assessing vendors should depend on multiple factors such as cost, payment terms, item availability, delivery speed, product quality, and vendor reliability.
4. Negotiate price and terms
Once you get suppliers’ quotes, examine them and negotiate wherever possible. Suppliers may offer flexible payment plans, product warranties, and other services. Once you agree with the vendor on the final terms, get a written agreement.
5. Create a purchase order
The next step is to fill out the Purchase Order form and send it to the vendor. It should be detailed with product specifications, rates, and quantities. The Purchase Order is a critical document.
6. Receive and inspect delivered goods
Once your order is delivered, it is time to receive it, and a quality check is conducted to ensure that the correct item(s) was obtained.
7. Approve the invoice and arrange payment
Conduct a three-way matching of purchase orders, goods receipts, and supplier invoices to ensure all is correct and to make payment.
Recordkeeping
Records should be stored properly. Using cloud-based software lets you manage and review documents from anywhere. When manual tasks are reduced, it leads to fewer errors and a smoother process.
Purchasing
Purchasing is more focused on short-term goals. It involves creating purchase orders, ordering goods, and arranging payments. Purchasing is a subset of procurement that involves processes or activities undertaken between the organization and the supplier. This process ensures that the required products are bought within the estimated timeframe and budget.
The key objectives of purchasing include generating a skilled team who work to lower the inventory of raw materials, reduce inventory management expenses, and find suppliers who can meet requirements. The purchasing department is responsible for maintaining purchasing records, resolving purchase-related issues, meeting sales representatives, and researching materials.
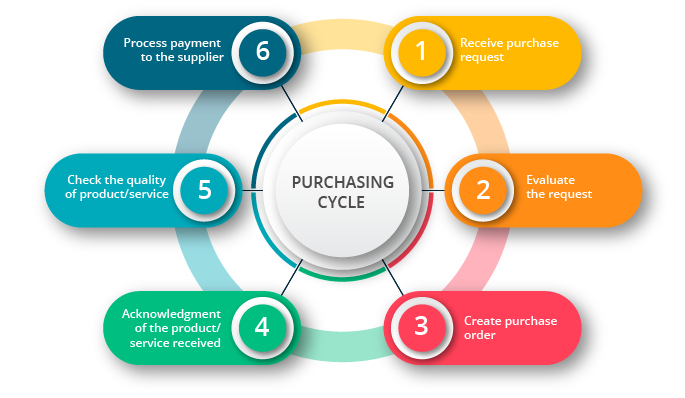
Steps in the Purchase Process
1. Receive and evaluate purchase requisitions
A purchase requisition is a document that details the deliverables required from the supplier. The purchase department evaluates the purchase requisition and approves it.
2. Raise and process a purchase order
In the next step, the purchase order is released. It details the contractual terms, payment terms, supply dates, and quantity of items.
3. Process and organize payment with the supplier
Once the organization verifies contract terms, it must ascertain order fulfillment and payment with the supplier.
Difference between procurement and purchasing
1. Scope
Purchase: It is a subset of procurement and is more transactional. It is a tactical process that deals with day-to-day functions, placing orders, and ensuring timely delivery. The main objective of purchasing is to focus on minimizing the order price.
Procurement: It involves strategic planning, supplier and risk management while focusing on relationships with suppliers and focusing on the company’s long-term goals. The main objective of procurement is to focus on the total cost of ownership and value creation.
2. Timeframe
Purchase: It focuses on short-term goals and meets the organization’s immediate needs. The purchase process ensures the execution of the procurement strategy on a day-to-day basis.
Procurement: It focuses on long-term goals. The procurement team analyses market trends, supplier relationships, and decision-making in the long-term.
3. Decision-making
Purchase: Decision-making includes managing order fulfillment, negotiating prices, and selecting suppliers.
Procurement: Decision-making involves evaluation and selection of suppliers, supply chain optimization, risk management, and more.
4. Relationship
Purchase: It emphasizes the transactional aspects of supplier relationships.
Procurement: It focuses on maintaining relationships with vendors and collaborating and communicating with them.
5. Risk Management
Purchase: It deals with more immediate risks related to delivery delays, price fluctuations, quality issues, and other routine tasks.
Procurement: It considers risk management factors such as geopolitical issues, supplier reliability, and price fluctuations based on market changes.
Conclusion
Procurement and purchase processes are related components of the supply chain, but procurement takes a broader, strategic planning role for a business. Purchasing is focused on the day-to-day needs of the company. Understanding these terms can help companies to enhance productivity and performance.
Follow Us