What’s covered in this blog:
- What KPIs are in manufacturing
- The difference between KPIs and metrics
- What determines a good KPI
- Why manufacturers should use KPIs
- The top 12 manufacturing KPIs and how to calculate them
- How KPIs can be made actionable
Manufacturing KPIs are quantifiable measures of production performance. They help manufacturers understand what they need to do to improve. They are the most critical metrics used by manufacturers to improve customer satisfaction, productivity, and lower costs.
What is the difference between KPIs and metrics?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) keep track of important measurements to help businesses make critical decisions. KPIs should relate to your business goals and help you understand how to achieve those goals.
KPIs are also metrics, but not all metrics are key performance indicators. Metrics measure how the business is doing in a specific area. KPIs are metrics that are the most essential for your business. Common KPIs tracked by companies are Revenue Growth and Profit Margins. But key performance indicators in production help ensure optimization in that area.
What defines a good manufacturing KPI?
1. It aligns with the company’s goals
All organizations have objectives they are striving towards. KPIs should align with your company’s goals to help measure your success towards those goals.
2. It is specific and measurable
With any KPI, it must define and measure something tangible so you can see if you are on track towards your goals. KPIs should be as specific as possible to be useful.
3. It provides achievable value
A KPI must be something that is achievable to provide true value. It has to be actionable, meaning the data it provides is used to make improvements as needed.
Why should manufacturers use manufacturing KPIs?
KPIs for production help manufacturers discover opportunities to increase customer satisfaction, improve competitiveness, and lower costs. By reviewing KPIs regularly, manufacturers can check on how they are measuring up with important metrics and make adjustments as needed.
The top 12 manufacturing KPIs and how to calculate them
There are lots of manufacturing metrics that can get used as KPIs. So what are the essential KPIs to use in manufacturing? And, how do you measure KPIs in manufacturing? The following are the KPIs we found to be used the most by our customers. What KPIs are important to your company will depend on its business strategy.
1. On-time Delivery
If manufacturers want to keep customers happy, they need to ensure on-time deliveries. Ideally, you want a 100% success rate. If deliveries are not being made on time, there could be a variety of reasons. Delayed supplies, an unrealistic production schedule, or frequent machine malfunctions are some examples. Having a high delivery success rate is important to keep current customers and attract new ones.
Calculation: On Time Units Delivered ÷ Total Units Delivered
2. Production Schedule Attainment
This helps manufacturers see if production was well-planned and if benchmarks are being met by workers. It allows manufacturers to determine if there are performance issues that impact deliveries. It isn’t enough to know if deliveries are being made on time. You must also determine what factors are affecting production so that they can be adjusted to improve delivery performance.
Calculation: (Actual Output ÷ Planned Output) x 100
3. Total Cycle Time
This KPI measures how long it takes for a customer order to be completed, from the start of production all the way to shipment. It does not include breaks or waiting time, just the actual time taken to manufacture the product. Total cycle time considers all factors in production, from raw materials to finished goods. It averages out the cycle times of all orders. Included in this metric is machine cycle time, which shows machine performance, and must be compared to the machine’s ideal cycle time.
Calculation: Net Production Time (NPT) ÷ Number of Units Produced
4. Throughput
This one lets you see how well your machines are producing. This KPI gets reviewed in real-time to resolve any issues before they become a bigger problem. Throughput works best when workers get assigned to machines they are skilled at operating. Also, throughput is at its peak when machines are kept in good working order and there are minimal touch points or steps that require the operator’s attention to manufacture the product.
Calculation: Number of Units Produced ÷ Total Time of Production
5. Capacity Utilization
This metric helps you determine if a machine is producing to its maximum capacity. Ideally, you want the machine to always be in good working condition with no downtime. Because production machinery is expensive, you don’t want it sitting idle. It’s important to have machines run at maximum capacity to increase efficiency and lower costs.
Calculation: (Actual Output ÷ Potential Output) x 100
6. Changeover Time
This tracks the time it takes to get everything done for a production run. Things such as unloading/loading, retooling, calibrating, and programming for the next job. Having this information helps manufacturers see areas for improvement. Maybe things can get better organized for setup, or maybe more staff training on the machinery is necessary. The faster the changeover time, the lower the cost to produce.
Calculation: Time to Produce First Quality Item in a Product Set – Time to Produce Last Quality Item in a Product Set
7. Yield
The yield KPI is also referred to as First Time Through (FTT). It measures how many products got manufactured without errors based on the total number produced. So if you had 10 products, but 1 was defective, you would have (10 – 1) = 9 ÷ 10 = .90 or 90% product yield without defects.
Calculation: (Total Items Produced – Defective Items) ÷ Items Produced
8. Scrap
Typically material that doesn’t meet quality standards is considered scrap. However, some manufacturers count any raw material that wasn’t used in production as scrap. Keeping track of scrap will help to keep costs down and produce better quality products.
Calculation: Total Scrap ÷ Total Product Run
9. Planned Maintenance
When determining the planned maintenance KPI, it’s important to factor in all emergency maintenance as part of the total maintenance. There should be less than 15% of planned maintenance that gets considered emergency work orders. Emergency maintenance is much more expensive than planned maintenance since it involves overtime, rushed parts, scrapped production, etc. It must be avoided as much as possible so it doesn’t cut into profits or cause headaches such as downtime and employee frustration.
Calculation: (Planned Maintenance Time ÷ Total Maintenance Time) x 100
10. Availability
Availability is the measure of machine uptime and downtime. It’s important to understand how much downtime your company has as it is costly and the biggest loss most manufacturers face. When calculating availability, it is essential that both planned and unplanned downtime get factored into the equation. It’s also important to keep track of the reasons for downtime. Those records can then be studied to identify areas for improvement.
Calculation: Uptime ÷ (Uptime + Downtime)
11. Customer Return Rate
This KPI is simple but important. How many goods are customers rejecting? It’s vital to keep a close eye on this KPI because returns not only cause a company to lose money by having to rework goods, but they can also hurt your reputation and customer retention rate. When goods are returned, it is critical to find out why and make corrections immediately.
Calculation: Rejected Goods ÷ Total Number of Goods Delivered
12. Overall Equipment Effectiveness
This critical KPI measures the ability of a piece of equipment to produce as an aggregate of availability, performance, and quality, but it doesn’t take into consideration when machines have downtime or maintenance is performed. So keep in mind this KPI doesn’t show the entire picture. You may see a high rate of effectiveness, but consider any underlying issues that may factor in.
Calculation: Availability x Performance x Quality
How do manufacturers make their KPIs actionable?
There is no point in measuring something if you don’t plan to use the information. It’s essential to take the KPIs that are most important to growing your business’s success and use them to make it better.
Key stakeholders should receive KPI measurement information. Use feedback from stakeholders to make improvements to your KPIs. KPIs should help you see where you are doing well, and where you could do better, so you can make changes. If your KPIs are tied to your business strategy, they can drive action that will lead you on a positive path.
Find the best KPIs for your manufacturing business.
These are not the only manufacturing KPIs, but they are some of the most used in the industry. Each business needs to use KPIs that work with its own strategy. And remember to use the information gained to improve profitability, competitiveness, and customer satisfaction.
What are the different KPIs in lean manufacturing?
KPIs important for lean manufacturing are those that focus on reducing waste or increasing productivity. Production schedule attainment, total cycle time, and scrap are some examples. Lean manufacturing KPIs also evaluate the progress of lean and process improvement initiatives or Kaizen.
Modern manufacturing ERP can easily track your KPIs
As a manufacturing business grows, it becomes difficult to track KPIs. It is also challenging to stay competitive without the right tools. Intelligent manufacturing ERP provides automation and the modules you need to run efficiently. It provides dashboards that show real-time metrics and KPIs to achieve business insight. Modern ERP has advanced functionality that lets you identify and capitalize on ways to increase productivity and revenue.
When using a manufacturing ERP system, it has pre-defined KPIs that can get used as-is, or adjusted to suit your business. Modern ERP has business intelligence that lets you analyze information to learn more about a KPI or to define more measurements for a particular situation.
KPIs should be used to help make important business decisions. Those using KPIs should take ownership over their specific manufacturing metrics and keep tabs on them to make improvements as needed. KPIs should change as necessary – for instance, to monitor a specific situation. KPIs should only track critical management issues. The number of KPIs for a business should be around 10, since too many can become unmanageable and ineffective.
OptiProERP with SAP Business One for Manufacturers
OptiProERP with SAP Business One is manufacturing ERP with attractive and practical dashboards where KPIs can be viewed in real-time. It provides many existing reports, or you can develop custom reports, to gather information for any KPIs you want to measure.
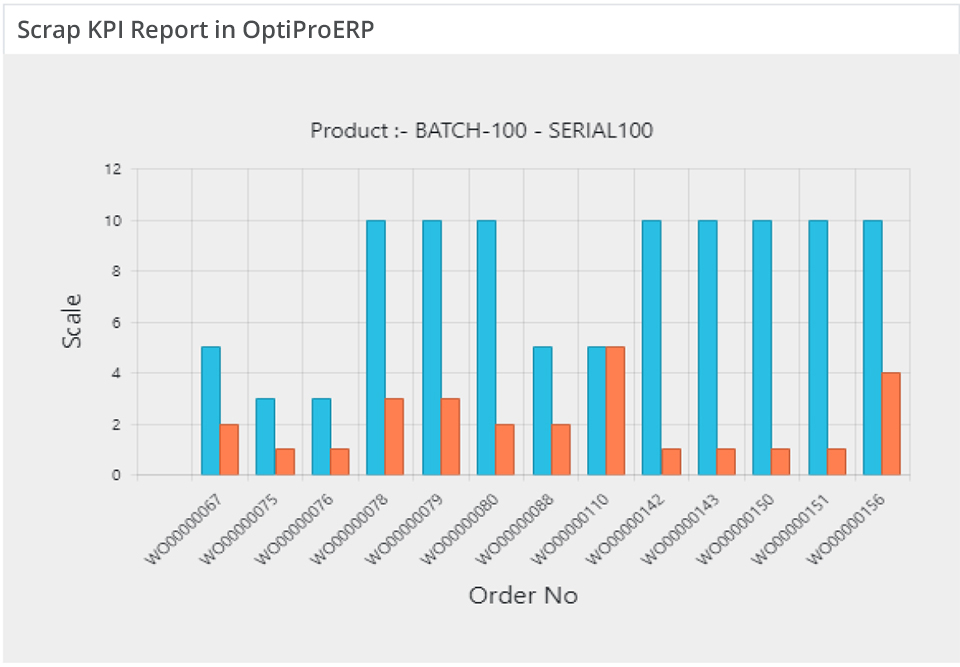
Interested in learning more about manufacturing KPIs and how OptiProERP with SAP Business One can help you achieve greater insight into your business needs? Contact us.
Follow Us