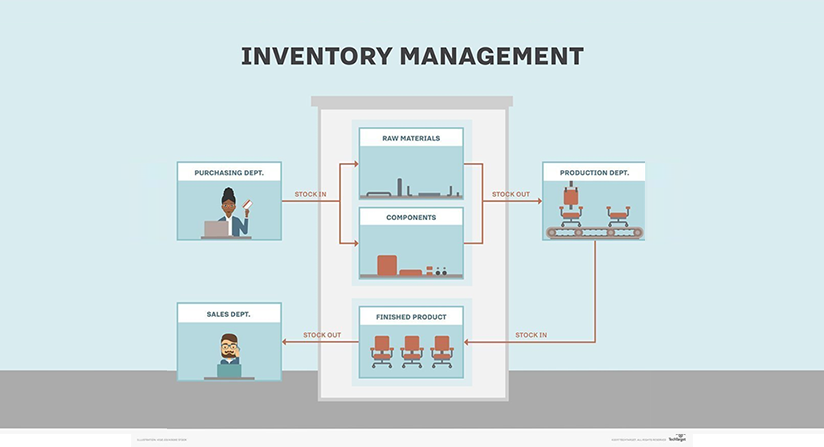
Manufacturing companies convert raw materials into a form that is of more value and use for the consumer.
Developed in the 60s and 70s, material requirements planning (MRP) offered an important breakthrough for shop floor managers. It linked production plans for finished goods with the requirements for the parts necessary to achieve those production plans. The basic idea was to ensure that enough stock of the correct components was on hand to build assemblies.
Recognizing that labor and machines also were key requirements for achieving a plan, MRP II (manufacturing resource planning), extended the idea of production requirements to include the number of labor and machine hours needed in the factory. However, providing insights and structure to address one set of issues revealed deeper and more complex challenges.
Building on the technological foundations of MRP and MRP II, ERP systems integrated business processes including manufacturing, distribution, accounting and finance, human resource management, project management, inventory management, service & maintenance, and transportation, to provide accessibility, visibility, and consistency across the entire enterprise.
What is Material Requirement Planning system?
Materials requirements planning (MRP) software plans for the production and purchase of the components used. MRP displays the number of components or materials required and when production intends to make or use them.
The material requirements plan establishes when the components/parts are needed to make each end item to be used in the final product. The planning horizon of MRP is at least as long as the combined purchase and manufacturing lead times.
MRP calculations were initially designed without any capacity checks or input from other departments. With that, the production plan was often not accurate, and few believed in this plan outside of the production function. The logic behind basic MRP software was later refined and is now knows as “Closed-loop MRP”.
These enhancements included capacity checks and incorporates programming to provide feedback on available capacity. Closed-loop MRP calculates the impact of each order on the work center that is scheduled to complete the order and if too little capacity is found at the work center it may change the order date. If this happens, other options available include sending the order to another work center or outsourcing it.
What is a Manufacturing Resource Planning System?
Manufacturing Resource Planning systems provide coordination between marketing and production. The marketing, finance, and production teams of the organization will meet and agree on a total workable overall plan expressed in this production plan.
Financial managers agree that having these manufacturing plans are very desirable from a financial point of view, and production teams also see these plans are crucial to meet the required demand.
The completely integrated planning and control system is called manufacturing resource planning, or MRP II. The term MRP II is used to differentiate the “manufacturing resource plan” (MRP II) from the “materials requirement plan” (MRP).
Marketing and production must work together on a weekly and daily basis to adjust the plan as changes occur. Order sizes may need to be changed, orders may be canceled, and delivery dates may also be adjusted. Marketing managers and production managers can also change production schedules to meet changes in forecasted demand. Senior management may adjust the production plan to reflect overall changes in product demand or resources availability/scarcity.
What are the benefits of MRP and MRP II software?
The primary benefits of MRP software are:
- Inventory reduction
- Efficient machine utilization
The benefits of MRP II software are:
- Strategic selection of carriers and routes
- Better research and forecasting
- Cross-functional integration in planning processes
- Better information flow throughout the organization
- Defined functional areas of the business
The connection between MRP, MRP II, and ERP software
The focus has shifted from internal optimization to external relationships generating the requirement for advanced ERP versions and modules. The need for efficiencies such as collaborative commerce and supply chain management has shifted the focus from cost reduction to business growth.
The below figure illustrates the number of areas in which ERP systems have expanded:
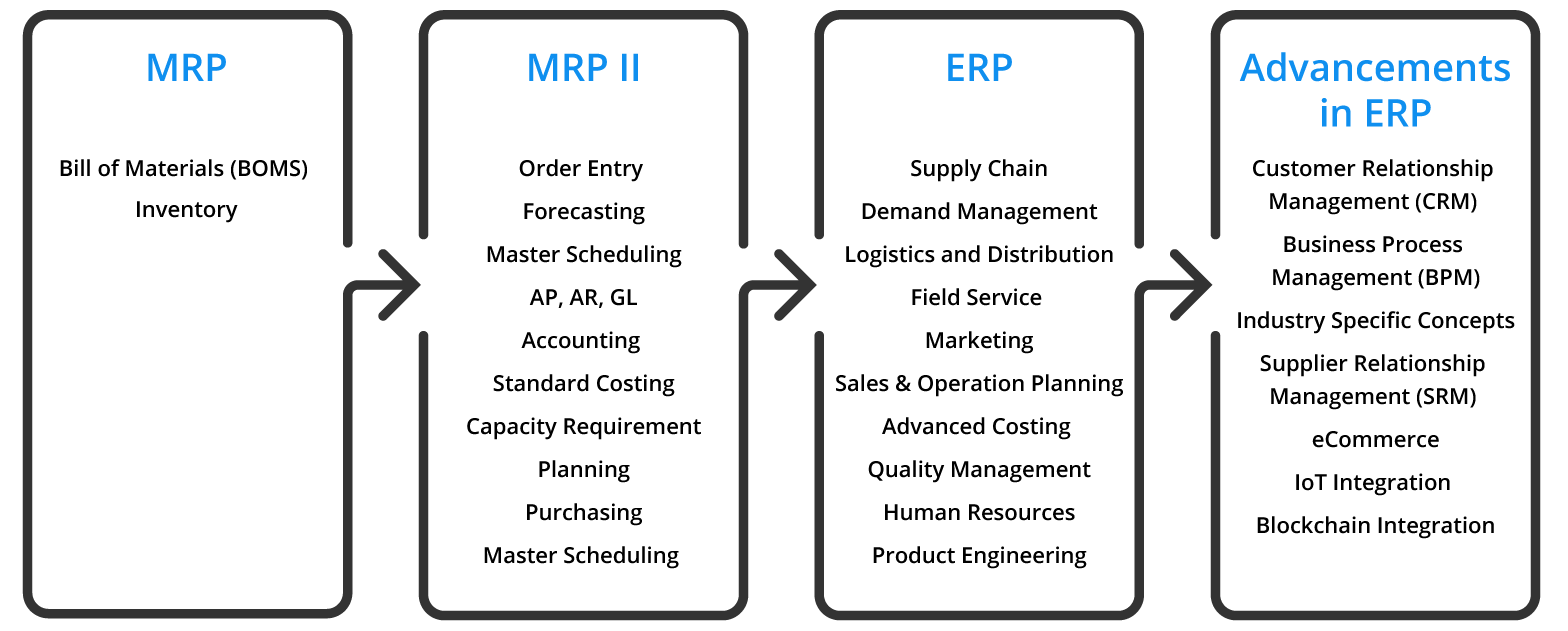
ERP’s are somewhat like the MRP II system, except ERP’s do not only focus on just manufacturing. The American Production and Inventory Control Society (APICS) defines ERP as the “Framework for organizing, defining, and standardizing the business processes necessary to effectively plan and control an organization so the organization can use its internal knowledge to seek external advantage.”
As the needs of organizations grew in the direction of a truly integrated approach toward materials management, IT systems began to match those needs. As these systems became both larger in scope and integration (when compared to the existing MRP and MRP II systems), they were given a new name enterprise resource planning or ERP.
Summary
Core functions of MRP software are designed to reduce inventory through better visibility, increased profitability, reduced cycle times and cash-to-cash cycle time, increased internal speed, availability of information, and reduced internal costs.
The core ERP processes focus primarily on finance, manufacturing, and distribution, enabling users to monitor and process customer transactions. Manufacturing ERP systems allow users to track orders, products, supplies, people and currencies. These ERP systems automate business processes increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Simply having MRP software will not sustain any competitive advantage a manufacturing business has to offer. Most organizations are now moving to an ERP solution to enhance supply chain efficiency and the overall velocity of their business.
To learn more about how an ERP solution can drastically change the way you work, feel free to reach out to us at www.optiproerp.com
General FAQ
What is Material Requirements Planning?
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a system responsible for planning and calculating the components required for manufacturing. It is a computer-based system that answers these questions – what is required? How much is required? And when it is required for manufacturing process?
What is Manufacturing Resource Planning Software?
Also known as MRP II, Manufacturing Resource Planning software is an integrated system that manages the planning of all the resources in an organization. It strengthens the coordination between marketing and production process.
What are the benefits of MRP Software?
Take a look at the benefits of MRP software:
- Better utilization of personnel and facilities
- Improved inventory planning and scheduling
- Higher customer satisfaction
- No overstock and stock-outs
What are the benefits of MRP II Software?
The primary benefits of MRP II software include: better quality control, improved cash-flow due to timely deliveries, better communication flow, defined functional areas in the organization and more. You can get consistent, real-time manufacturing data available on the screen.
Follow Us